
These results support our previous studies which revealed separate mechanistic regions for PCET reactions and also assigned phenol oxidation by 3+ at low pH to a stepwise PCET mechanism. NOTE: If your steam library is on another drive, it will have a different, but. The stepwise mechanism remains competitive despite a significant change in the p K a and redox potential of the phenols which leads to a span of rate constants from 1 × 10 5 to 2 × 10 9 M -1 s -1. The proton transfer tunnel lining along the direction of the proton gradient across the membrane, with D149 immediately transferring a proton from D45 to bulk, can provide a constant driving force for the excess proton leaving D324 moving toward D45. C:Program Files (x86)SteamsteamappscommonFINAL FANTASY XIV - A Realm Reborn.
DRIVING FORCE FOR PROTON TRANSFER DRIVER
In most states and provinces, having a display within view of the driver that shows video while the. This is in contrast to the concerted or proton-first (PTET) mechanisms that often dominate at higher pH and/or with buffers as primary proton acceptors. Follow this link to get started using Proton VPN. Inverted region behavior, where the rate constant decreases as the reaction becomes more exoergic (i.e., as G 0 becomes more negative), has been observed. From an analysis of the kinetic data using a Marcus-type free energy relationship, we propose that our model system follows a stepwise electron transfer-proton transfer (ETPT) pathway with a pH independent rate constant at low pH in water. The driving force dependence of the rate constants for nonadiabatic electron transfer (ET), proton transfer (PT), and proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET) reactions are examined.
DRIVING FORCE FOR PROTON TRANSFER SERIES
We examined PCET between a series of phenol derivatives and photogenerated 3+ in low pH (≤4) water using the laser flash-quench technique. The initial proton transfer involves a water molecule (H2O) and a subsequent hydronium ion (H3O+) via the hydrogen bonding between the aqueous media and the.
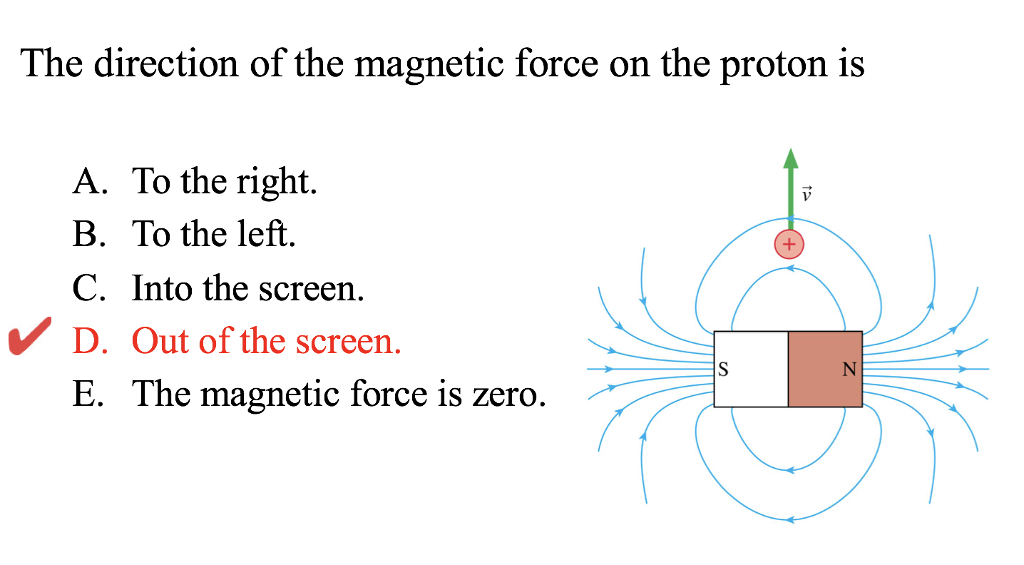
Proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET) from tyrosine and other phenol derivatives in water is an important elementary reaction in chemistry and biology.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
